The world we live in is becoming more and more digitized every day. In business, digital marketing has completely transformed the way we operate. Social media and the internet have dismantled space and time restrictions, democratizing opportunities for many enterprises, regardless of size.
While that’s definitely a great thing, the shift from brick-and-mortar to the digital space has created an uber-competitive marketing landscape. As a business owner or marketer worth your salt, a digital marketing strategy that will keep you in the running is no longer just an option. A quick Google search for the most effective online marketing game plans will likely churn out “Search engine optimization” or SEO and “search engine marketing” or SEM. So which one should you go for? We’ve drawn up this comprehensive guide to help you decide the best-fit strategy for your company.
Why are SEO and SEM important?
Nowadays, instead of driving to the shops and browsing through stacks of merchandise in physical shops, most people simply go online to get what they need. Although there’s still no substitute for face-to-face interaction, the popularity of online activities as a convenient means to connect with others or pass the time is also vastly increasing.
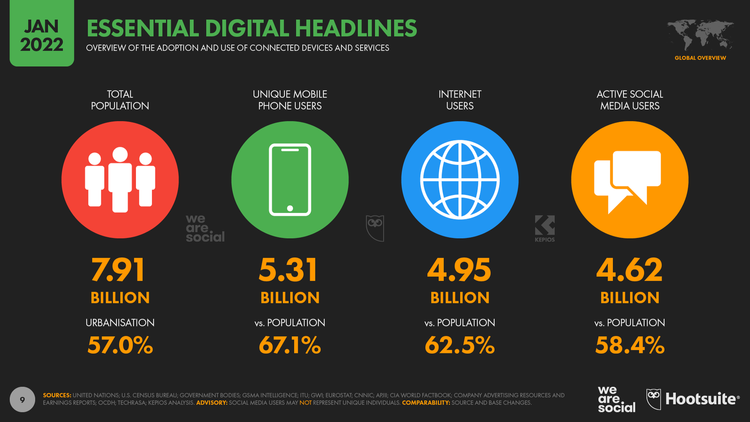
A 2022 report reveals that there are now 4.95 billion internet users globally, and this is growing at a yearly rate of 4% (half a million new netizens daily). If you consider that the average internet user from the 16-to-64-year-old bracket spends close to 6 hours online every day, the marketing potential can be mind-boggling.
With SEO and SEM, you can take advantage of the íncreasing relevance of the online space. These strategies devise ways for you to improve your brand’s searchability. With the right keywords, they drive traffic to your website. If you do well in online search, the more site visitors and opportunities you have to increase awareness for your brand and grow your business. So, in the contest of SEO vs SEM, which is better?
SEO vs SEM Comparison: The Key Difference
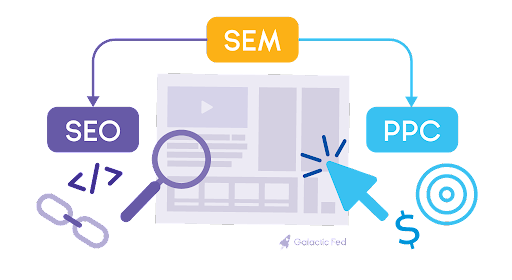
SEO vs. SEM marketing? Although they’re often used interchangeably, SEM is actually the broader concept of the two, referring to both paid and organic search tactics. It’s a strategy encompassing all activities and tools to optimize your website’s visibility, such as boosting search engine results pages or SERP performance. SERP is the page that shows up when you enter a search query into Google, Yahoo!, or other search engines.
On the other hand, SEO improves your online visibility through organic search techniques, when prospects look for products or services in search engines. Throughout the customer’s search journey from the time they go on the internet to the moment they get converted, your company need not pay anything.
An SEM Overview
Unlike traditional marketing, such as billboards, print, and broadcast, SEM strategy grows your business online. It figures out how search engines work and uses both paid and organic techniques so your brand can easily be found on the internet. It’s true that offline marketing still exists, but SEM is becoming increasingly more relevant, trumping traditional marketing in many respects. Although the cost may appear substantial at the outset, with agency packages typically averaging a few hundred or thousand dollars, SEM can prove to be more cost-effective in the long run. Additionally, SEM results are more trackable, with analytics tools monitoring clearly defined metrics, ensuring that you get your money’s worth.
The SEM strategy is split into two subsets. First, as we’ve discussed earlier, SEO refers to organic SEM. The second type of SEM is PPC or pay-per-click, pertaining to paid SEM. Let’s drill these down a bit further.
How does SEO work?
SEO is the SEM strategy that targets organic traffic. Organic refers to authentic marketing activities that naturally build awareness around your brand and drive traffic to your site. This costs relatively little (compared to PPC), although you may have to invest in people to conduct keyword research, create content, etc.
If you take pains in ensuring that your site is well-optimized and follow SEO best practices, your business or brand may turn up on first-page results. Once someone enters a query and clicks on the search outcome (hopefully yours!), then they’re driven to your site, where there’s a higher chance of a conversion. Or it can also be that they’re just browsing interesting content and end up clicking relevant keywords to get more information. If those keywords link back to your site, you’ll gain a visitor—and a prospective customer. It may look simple enough, but appearing on that critical first page takes time plus several effective SEO strategies.
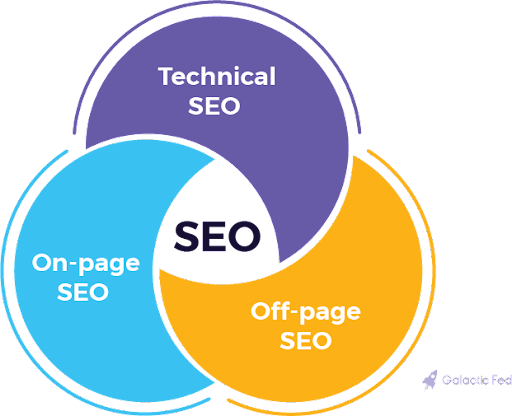
3 Types of SEO
SEO is categorized into three types: on-page, off-page, and technical. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
1. On-page SEO
On-page SEO refers to digital marketing activities on your site to optimize your pages and enhance searchability. Typical examples are producing quality content, crafting meta descriptions and highly relevant title tags, using internal links, and optimizing keywords, images, and URLs. All these efforts should make your page attractive to search engines.
Having high-quality content is essential in making sure that users are drawn to your site and stay long enough to take the necessary actions for conversion. If they don’t find anything of value from the very first page, they’re likely to get off it right away. This will lead to poor bounce rates for your site ( the percentage of visitors who leave after just looking at one page), leading to bad user experience in organic search.
2. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on your website’s architecture. It’s more concerned with the robustness of your backend structure rather than the content elements of your page. As a result, technical SEO can help make your pages load faster, increase mobile-friendliness, and enhance site security. It also aims to improve user-experience and make it easy for search crawlers to understand and index your pages for search rankings.
3. Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO is the reverse of on-page SEO, pertaining to activities that take place off your site. This strategy aims to set up your webpages as reputable by associating them with other authoritative sites. Off-page SEO examples include link building (to increase your pages’ relevance), social bookmarking (links of web pages are saved for easy retrieval), and free local listings (these supply contact details and other valuable information about your business).
9 SEO Key Metrics
Below are some of the most commonly used metrics, so you’ll know if your SEO tactics are working.
1. Time-on-site
This is basically the length of time a visitor spends on your webpages, from the time they click through a search engine or an off-page link leading to your landing page to the time they leave your site (as measured by timestamps). A good duration for a session would be between 2 to 3 minutes, which is enough time to increase interactions between the prospect and your brand.
2. Organic Traffic
Organic traffic is the natural flow of visitors from unpaid sources to your site. If you have great content and the keywords used to search are a great match to your pages, the algorithms will rank you high in organic search, driving more visitors to check out your pages. SEO analytics tools such as Google Analytics or SEMRush can help you measure your organic traffic.
3. Pages Per Session
This metric is often referred to as “page views per session.” To compute this metric, divide the number of page views by the total number of sessions. A session, also called a “visit,” is a set of interactions made by a user with your site within a specific period. It can include page views and payment transactions. A high page-per-session score shows that users are interacting and engaging with your site.
4. Click-through Rate
A click-through rate or CTR measures how often users click on a link compared to the number of page views. This is an important metric because it can help you understand your customers better, indicating what works for them and what doesn’t. A good organic CTR ranging from 3% to 5% shows that your SEO campaign is effectively driving people to your site.
5. Exit Rate
In contrast to a bounce rate which refers to first-page sessions, an exit rate shows how often visitors leave your site after visiting any number of pages in the same session. The prospective customer may have taken further action beyond going through your home page but has exited your site from a particular page before concluding the desired action (such as making a payment). This can help assess the improvements needed for that specific page.
6. Core Web Vitals
Core web vitals are metrics that score a user’s experience on your site. These measure the following:
- Page load performance: Ideal is within 2.5 seconds
- Interactivity or how quickly users respond to the content: A good number is within 100 milliseconds.
- Visual stability: No elements on the page should suddenly shift as users go through the content. A score below 0.1 indicates a high-quality user experience.
To secure your core web vitals, you may go to the web-vitals open-source library or check out PageSpeed Insights.
7. Backlinks and Referring Domains
The referring domains and backlinks that your site has are also measured by search engines to establish your site’s authority. Referring domains are also known as linking domains because they contain backlinks that drive traffic to specific pages on your site. Backlinks allow pages from one website to link to another site’s web pages. So if an external link leads back to you, then you have a backlink from that site. This metric is crucial because it tells Google that the content in your site is valuable as an authoritative resource, giving your webpages a vote of confidence and boosting your rankings. SemRush offers tools to measure backlinks analytics and domain authority scores.
8. Keywords Ranking
Keywords are the words people enter as queries into search engines. The goal is for your website to rank high in the keywords that are most relevant to the products or services you offer. For this to happen, you must do the necessary keyword research and ensure that your site is optimized so search engines can easily understand and index your keywords. To determine if your keyword strategy is working, you’ll need to track your performance closely. For the most accurate results, use an efficient rank monitoring tool like Ahrefs’ Rank Tracker.
9. Crawl Rate
This metric measures the number of pages from your site that are “crawled over” or read by search engine crawlers (called bots or spiders). Their intent is to find out what your site is about and also detect any changes. You’d want Google to consistently crawl your pages so they can be indexed (and re-indexed!).
Indexing is how search engines discover new content and add them to the searchable index. The thing is, your pages will only be indexed if you have quality and optimized content, which includes having relevant title tags, meta tags, and alt descriptions for images. You can find your crawl stats by logging into Search Console.
What is PPC, and how does it work?
Suppose you want to immediately serve up your ads to individuals who are already looking for your products or services. In that case, the other SEM strategy alternative, PPC or pay-per-click, may be what you need. PPC, also known as Paid SEM, covers all digital marketing activities that you pay for. You want to optimize your ad budget by using the best PPC tactics. Unlike SEO, where you get “free” traffic once your site is more or less established, search engines charge your brand every time users click on your ads.
B2B companies optimize their ad placements when users’ intent is already at a more advanced level (meaning they’re in the decision-making phase instead of simply navigating). Here are other PPC strategies that you can deploy to make the most of your ad budget.
4 PPC Strategies
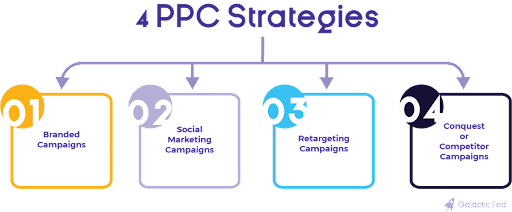
1. Branded Campaigns
A branded PPC campaign revolves around a tightly coordinated set of keywords along with your company’s name and other brand elements. This involves bidding on your branded keywords so that you can edge out competitors who may want to invade your territory. Another great thing with branded campaigns is that you can craft your message and control what gets to be seen on the SERP, ensuring that you communicate whatever is most relevant to your business. At the same time, this strategy can be more cost-effective, allowing you to bid and use narrower keywords that have less competition and can give you more qualified leads.
2. Social Marketing Campaigns
On average, we spend about 2 1/2 hours every day on social media, making it one of the biggest influencers of the 21st century. Social marketing PPC campaigns hinge on the power of social media to boost brands. Here, ads are placed on social media platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and WhatsApp. One advantage of such campaigns is that you’re able to target who will see your ad based on interests, demographics and subcultures, and spending power and patterns.
3. Retargeting Campaigns
Retargeting campaigns can make your brand look larger than life by making your presence ubiquitous. Say a prospect “falls through the cracks” of your pages or your referring domain, leaving unconverted. When you invest in a retargeting campaign, that prospect or lapsed user will see your ads pop up whenever they’re online, allowing more opportunities for re-engagement. This technique zeroes in on customers with a previously established user intent who are more likely to convert than new users. Thus, this popular PPC strategy has more chances of winning.
4. Conquest or Competitor Campaigns
If you have both a branded and a conquest campaign, you’ve got sort of a bookend strategy. While branded campaigns cover search queries for your brand and brand elements, conquest ads are campaigns that will place your company’s ads in search results for your competitors or other related products or services.
7 PPC Key Metrics
Although some PPC strategies can be cost-effective, allowing you to group specific keywords so you can maximize your paid ads, you may still have to shell out a pretty good amount. Therefore, ensure that your chosen PPC campaigns deliver results by assessing them against these metrics.
1. Average Cost Per Visit
This pretty straightforward metric shows how much you’re paying for every visit to your pages or site. Your digital marketing strategy may be using different platforms for different reasons, from boosting brand visibility to targeting leads at the bottom of the purchase funnel. Each of these also differs in pricing and traffic volume. To get your average cost per visit, divide your total ad spend across all platforms by the total number of site visits. This will help you track your ad spend and assess the effectiveness of your campaigns.
2. Cost Per Click (CPC)
Cost per click is a universal digital metric that tells you how much you’re paying for each click in your PPC campaign. Every time your text or display ad gets a click, this indicates that your brand or product is getting attention from someone who may be interested in what you have to offer. CPC rates vary with the type of business. Prices also depend on such factors as your ad rank and your competitors’, your quality score (which we’ll get to in a bit), and the maximum bid (the highest amount you’re willing to pay for an individual keyword or a whole set of them). Nonetheless, the average CPC across industries is estimated at $2.
3. Impression Share
Impression share is another key PPC metric. An impression, also called a view-through, happens when a user opens an app or visits a website and sees a thumbnail ad, regardless of whether or not they click on it. Essentially, it tells you how often an ad shows up compared to how often it could have appeared as an eligible search or view on the Google Display Network. For digital marketers, the impression share metric helps them gauge the reach of a particular advertising channel. It can also help determine how frequently ads show up in the ads auctions on search results.
4. Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is among the most accessible metrics to understand. It simply refers to the percentage of people who click on your ad and are convinced to perform and complete the desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a free trial. If you’ve achieved a conversion rate of 10%, this shows that your PPC campaign is highly effective.
5. Cost Per Conversion Rate
Once a customer is converted, you’d want to determine how much that cost you and if it was worth it. This is where your cost-per-conversion metric can come in handy. To compute it, divide your total ad spend for a particular campaign by the total number of conversions for the same period, and then multiply by 100. If the resulting figure is too high, this may mean that you’re focusing on the wrong target audience or that your ad isn’t compelling enough.
6. Click-through Rate (CTR)
This measures how many clicks you have compared to your page or ad views (impressions). Knowing the click-through rate shows that your campaign delivers the highest possible number of people to your product or service. Additionally, a good CTR will get you a high-quality score (the next item we’ll discuss), which then helps push up or retain your ad position for more pricing discounts from Google and other search marketing platforms. On the flip side, a high CTR for keywords that aren’t relevant to your business can hurt you, costing you a lot (remember that you pay per click?) without anything to show for the considerable expense.
7. Quality Score
Google rates the quality of your keywords and ads by assessing their click-through rate, relevance, and landing page experience (e.g., how fast your page loads and how easy it is to navigate your site). This metric compares how your ad is doing compared to others on a scale of 1 to 10. You may check for your ad’s relevance on Google and Facebook ads’ diagnostic tools.
SEO or PPC: Which one is the best SEM strategy?
Both SEO and PPC are strategies that can work for you depending on your specific business goals and objectives. If you must choose only one, we’ve outlined the advantages of each one below.
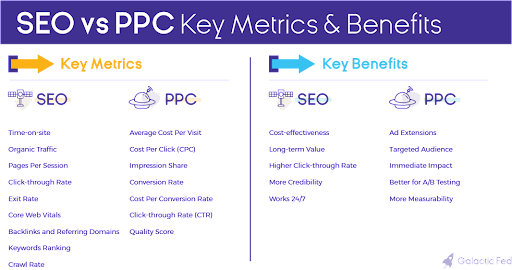
The Benefits of SEO:
1. Cost-effectiveness
Startups with budget limitations, especially at the initial stages of getting operations off the ground, may find SEO more appealing than PPC. Although you’ll still have to invest in a team who’ll create content, conduct outreach (your backlinking tactics), and speed up and optimize your site, you won’t have to spend on any ads on the search engines.
2. Long-term Value
If you’re to put the two strategies in a race, PPC would be the dazzling sprinter, needing bursts of energy (cash, i.e.) to stay in the game. When the ad spend dries out, and the ads are switched off, then you’re “stopped in your tracks.” On the other hand, SEO would be the reliable marathoner, able to sustain you in the long term by strengthening your domain authority. And like endurance runners whose speed improves the longer they stay in the race, SEO can position you more strategically, increasing value and building growth momentum over time.
3. Higher Click-through Rate
One study of billions of Google search results shows that the first organic result has a click share of over 25%. So if you’re using SEO and you land among the top outcomes on the first page, then you’re likely to beat paid SEM ads. You will, however, have to put in the necessary time and effort to land on that first page that will get you more click-throughs.
4. More Credibility
Between a trusted friend’s advice and a paid ad, which one will you most probably take? You’ll most likely pick the former. Same thing with SEO. Because it’s organic and perceived to be without a commercial agenda, people see it as more authentic and credible. However, do note that the keyword here is “trust.” You need to earn this by first establishing your expertise and credibility in your chosen industry so users will be drawn to your site. Then, you’ll have more opportunities to convert them into customers.
5. Works 24/7
SEO never sleeps. It works day and night to drive traffic to your website. This is in contrast to PPC, which only has an effect while its ads run. Since PPC can be costly, you may need to have a specific ad schedule and be highly strategic with your placements.

The Benefits of PPC:
1. Ad Extensions
If you’re using PPC, you can increase your advantage by getting ad extensions. They give more information, make your ad more attractive, and increase user interaction with your brand. For instance, one extension can show pricing while another can provide your business location. You may also avail of call-out extensions, additional text snippets that highlight more of your brand’s features and benefits.
2. Targeted Audience
You can choose which exact audience will see your ads with PPC, unlike in SEO. This means you can fine-tune your target demographic (by age, gender, average income, and so on). Here, you can also use both first-party data (collected through your site) and third-party data ( from external sources) to better segment and understand the specific market you’re going for. This helps you enhance the quality of your leads and optimize your ad budget.
3. Immediate Impact
Do you want to rank #1 in a Google search result for your desired keywords ASAP? Then use PPC. As soon as you pay for your campaign, your ads will start showing front and center in SERPs. This is particularly helpful in boosting low organic search results or if you just can’t wait for your digital marketing strategy to kick in.
4. Better for A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is basically a random experiment that helps you quickly determine which of two web page or app versions work better or is preferred more by users. Through PPC, you can leverage A/B testing to get information on how to improve the design of your site and ad copy and immediately make the changes to increase user engagement and conversion. You can even use this to check the viability of a concept or promo before going forward with it, even switch strategies if necessary.
5. More Measurability
Because you pay for your ads, unlike in an SEO strategy, you can directly evaluate and monitor the effectiveness of campaigns and assess your ROI. You are in total control of what goes on in a PPC campaign. You ultimately determine who sees what, when, and how, and the amount of ad spend.

How much do SEM and SEO cost?

As we’ve discussed earlier, you do get free traffic from SEO. But, you’ll need to invest in the right people and apply the best SEO techniques to help you create and deploy your strategy and rank well in SERP. To do this, your team can leverage paid SEO tools, such as Ahrefs, to conduct keyword research, gauge the traffic potential of a topic, and even track competitors’ sites. These tools can cost as little as $99 (for the most basic services) to as high as $5,000 (for the more sophisticated platforms).
Although the average SEO spend is pegged at $750 to $2,000 every month for small businesses, it really boils down to what your goals are and how much time you have. The good news is that much of this is upfront. So, once you start ranking, you don’t need to break the bank to maintain your position.
In contrast, a PPC campaign can cost you anywhere from zilch to as much as you have available to spend. Rates vary depending on the industry. You may choose to allocate a minute portion of your total marketing budget on PPC but expect little traffic as an outcome. Of course, your overall business strategy and aggressiveness will also decide the PPC budget that you need. Although there are starter packages in the range of $900 to $1,200, on average, SMEs may need to invest between $9,000 to $10,000 monthly to make their PPC campaign work.
How long does it take to get results for SEO and SEM?
With SEO, you can expect to see results in 6 to 12 months. It’ll even take longer (an average of 2 years) if you want to rank on the first page of search engines. This is because Google needs time to become familiar with your site before recognizing you as a trustworthy and authoritative domain. However, it’s possible to perform better in a shorter period of time depending on the SEO practices you employ.
SEM, on the other hand, has an instantaneous turnaround time. Launch your campaign right now, and in a few hours (sometimes, even less than an hour), your ads may already be popping up on your target audience’s screens. The caveat is that, although it’s possible to realize near-immediate individual conversions, you’ll probably land a worthwhile ROI in a couple of months more from the time of launch.
SEM vs SEO vs PPC: Which one should I use?
Still, perplexed as to which strategy to use? Let’s get to the bottom of the SEM vs SEO vs PPC dilemma.
Focus on SEO if:
- You don’t have a regular monthly ad budget or don’t want to rely too heavily on a paid digital marketing strategy.
- You have the time to wait it out before seeing your ROI (especially if your site is new).
- You’re in an industry where there are abundant opportunities for more organic content.
- You’re already established and are seen as an expert resource.
Focus on PPC if:
- You’ve allocated a consistent ad spend monthly.
- You want to rank in SERP right away.
- You have plenty of competition for your target keywords in your industry.
- You’re just starting out, and you have little online presence.
When should you use both SEO and PPC?
What if you can do organic and paid SEM simultaneously? Then, by all means, go for it! Both SEM approaches can actually optimize the other. For instance, SEO can be foundational to your PPC strategy, making it work more effectively by ranking you higher in SERP, landing you better-quality traffic, and increasing your conversions.
Alternatively, PPC can boost your SEO strategy by helping you hone in on your target audience. This way, your SEO strategies can be more deliberate, saving you precious time and effort.
Ramp up your SEO and SEM game
Whether you’re looking to secure your footing in the digital space or searching for ways to intensify your game, the right growth marketing agency can make it happen. Our world-class team at Galactic Fed can help you craft your strategy, deep-dive into your analytics, and create content that converts, so you get only the results that you need and want. So take that one small step for your brand, and see that giant leap for growth. Book a free 30-minute consultation with us today!

